Blocked Fallopian Tubes: Symptoms, Causes
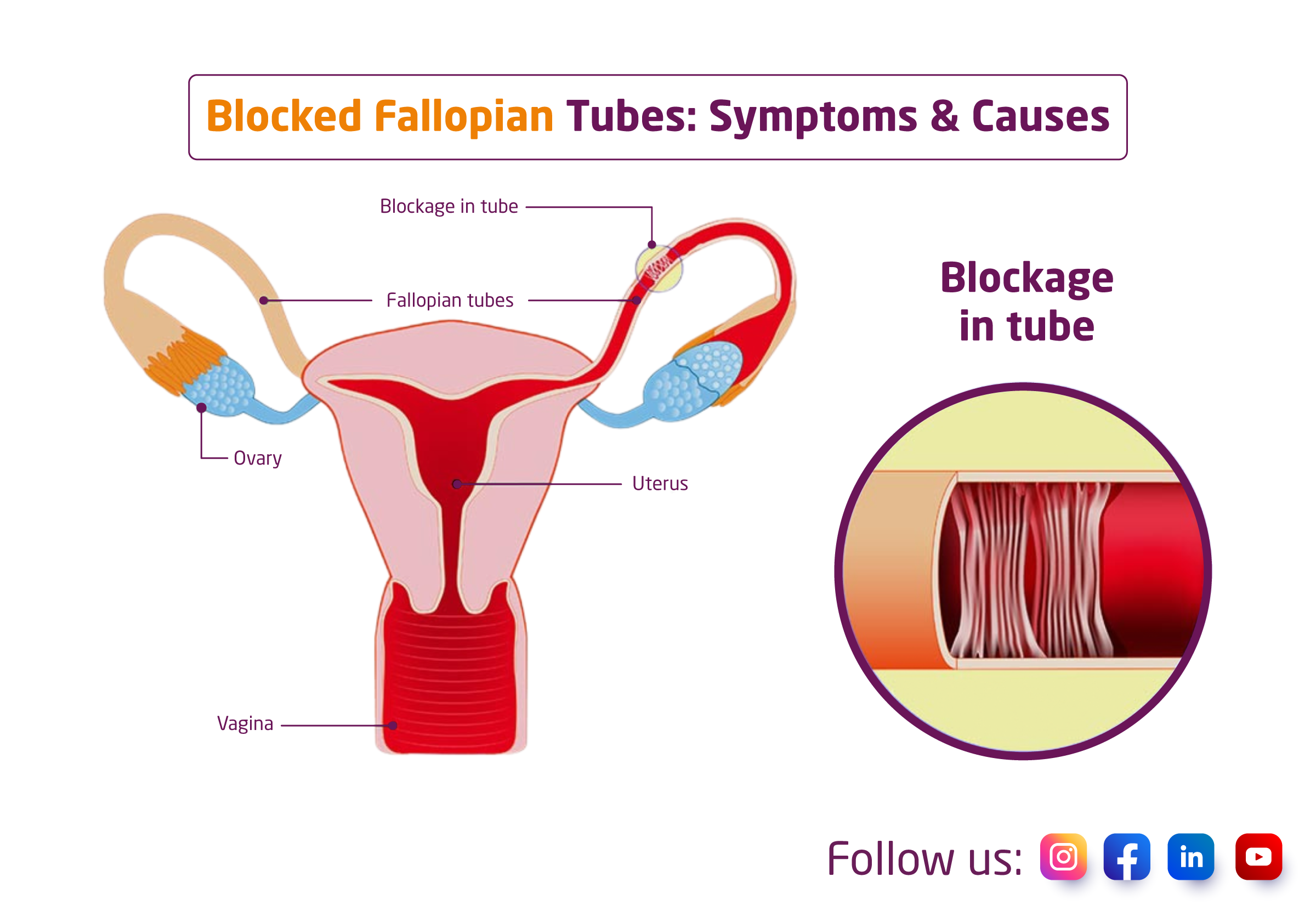
Fallopian tubes are part of the female reproductive system attached to the uterus from one side and ovaries on the other. Every month, an egg is transported from an ovary to the uterus by the fallopian tubes during ovulation, which takes place around the middle of a menstrual cycle. The fallopian tube is where conception also takes place. If a sperm fertilises an egg, the fertilised egg travels via the tube to the uterus where it will be implanted.
A blocked fallopian tube prevents sperm from reaching the eggs and the fertilised egg from returning to the uterus. Scar tissue, infections, and pelvic adhesions frequently cause fallopian tube blockages.
What are the symptoms of a blocked fallopian tube?
Contrary to anovulation, which may be indicated by irregular menstrual periods, obstructed fallopian tubes rarely result in symptoms. Infertility is frequently the first “symptom” of obstructed fallopian tubes. In addition to regular routine fertility testing, your doctor may order a special X-ray to check your fallopian tubes if you haven’t been pregnant after a year of trying (or after six months if you’re age 35 or older).
Lower abdomen pain and unusual vaginal discharge are possible indications of a particular type of obstructed fallopian tube termed a hydrosalpinx. However, not all women may experience these signs. When a blockage causes the tube to expand (grow in diameter) and fill with fluid, the condition is known as hydrosalpinx. Fertilization and pregnancy are prevented because the fluid inhibits the sperm and egg.
Blocked fallopian tubes can have a variety of causes, some of which may also have unique symptoms. For instance, painful menstruation and painful sexual activity may be brought on by endometriosis and pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
What are the causes of a blocked fallopian tube?
PID most frequently brings on fallopian tube blockages. Although not all pelvic infections are associated with STDs, pelvic inflammatory disease results from a sexually transmitted illness. A history of PID or a pelvic infection also raises the chance of blocked tubes, even if PID is no longer present.
Here are some more factors that could result in obstructed fallopian tubes:
- Having chlamydia or gonorrhoea currently or in the past is an STD infection.
- An abortion or miscarriage-related uterine infection history.
- Previous fallopian tube surgery, including tubal ligation.
- History of an appendix rupture.
- History of abdominal surgery.
- Previous ectopic pregnancy
- Endometriosis
How to diagnose a blocked fallopian tube?
It can be challenging to recognise blocked fallopian tubes. It is sometimes difficult to determine if the tubes are obstructed or closed because they can open and close.
- a hysterosalpingogram (HSG), an X-ray examination: Injecting a safe dye into the womb should cause it to flow into the fallopian tubes and the pelvis. On an X-ray, you can see the stain. The fallopian tubes may be blocked if the fluid does not enter them or does not spill put freely into the pelvic cavity.
- a sonosalpingography (SSG), a type of ultrasound examination: Fluid is pushed through the cervix into the uterine cavity to see if it comes out in the pelvic cavity. While doing an ultrasound this fluid can be seen flowing into the cavity and out into the pelvis to determine if the tubes are opened.
- laparoscopy, often known as keyhole surgery: A small incision is made in the body, and a tiny camera is inserted to obtain images of the fallopian tubes from within. Dye is pushed into the uterus to see if it flows out in the pelvic cavity.
How to treat blocked fallopian tubes?
Fallopian tubes that are obstructed may be surgically opened. However, this depends on the degree of scarring and the location of the blockage.
What are the possible complications caused by a blocked fallopian tube?
The same risks are involved with surgery to open the fallopian tubes. These consist of:
- development of more scar tissue.
- bleeding.
- infection.
- ectopic pregnancy.
Takeaway
Even while blocked fallopian tubes can lead to infertility, it is still possible to become pregnant. Oftentimes, laparoscopic surgery can clear the obstruction and help fertility. IVF can assist you in getting pregnant if surgery is not an option. Ferticity IVF & Fertility Clinics is one of the best IVF facilities in Delhi which has a cutting-edge laboratory and a competent staff of specialists in both fertility and medicine. Book an appointment with us today!