According to the World Health Organisation, around 17.5% of adults experience infertility globally, representing roughly 1 in 6 people worldwide. This growing challenge has positioned assisted reproductive techniques like IVF as a reliable medical solution for couples unable to conceive naturally through standard methods.
In vitro fertilisation (IVF) fertilises eggs outside the body in controlled laboratory conditions before transferring the resulting embryos into the uterus. This guide explains the IVF procedure step by step through five medical stages spanning from ovarian stimulation to final embryo placement.
What Are the 5 Stages of IVF?
The IVF treatment process consists of five steps. These stages aim to help with fertilisation and embryo development before starting a pregnancy:
- Ovarian Stimulation
- Egg Retrieval
- Sperm Collection or Retrieval
- Fertilisation and Embryo Development
- Embryo Transfer Procedure
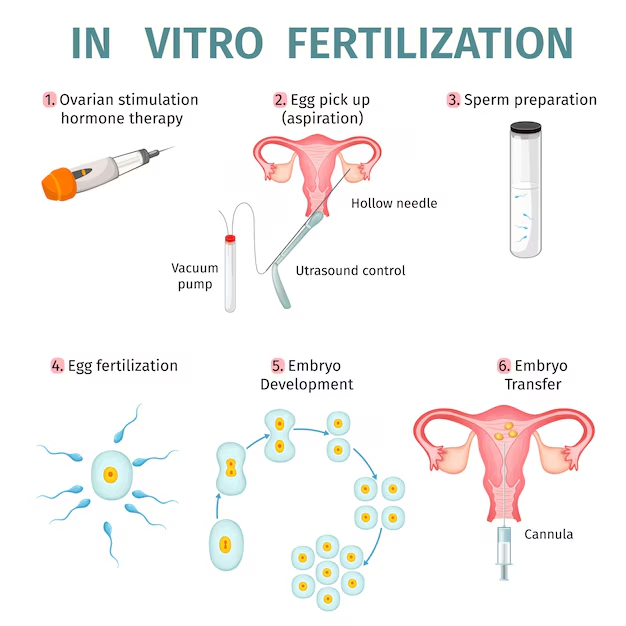
1. Ovarian Stimulation
Fertility medications stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple mature eggs during one menstrual cycle instead of the single egg released naturally each month. This test tube baby process begins with hormone administration to boost egg production for fertilisation attempts.
- Medications Used: Doctors prescribe injectable follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinising hormone (LH) to trigger multiple follicle growth simultaneously. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonists prevent premature egg release during the stimulation phase.
- Monitoring Progress: Transvaginal ultrasound scans measure follicle size every 2 to 3 days throughout treatment. Blood tests track oestradiol hormone levels to confirm proper egg maturation and prevent ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome complications.
- Duration: Stimulation continues for eight to fourteen days based on individual ovarian response to prescribed medications. Doctors adjust hormone dosages according to follicle development patterns observed during monitoring appointments.
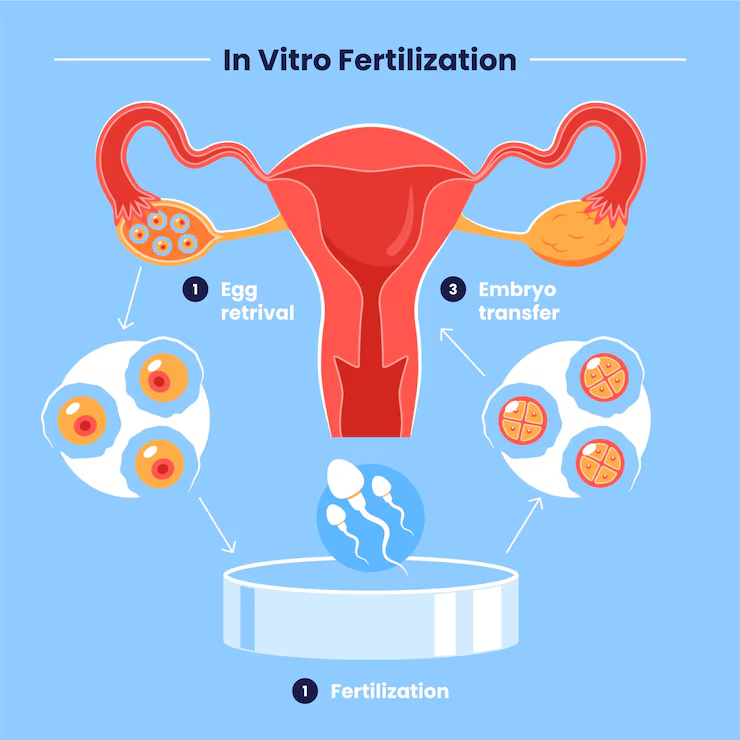
2. Egg Retrieval
Mature eggs are collected through minor surgical intervention performed under conscious sedation or general anaesthesia in outpatient facilities. The IVF procedure requires precise timing for optimal egg collection.
- Timing: Patients receive a human chorionic gonadotropin trigger injection exactly 36 hours before the scheduled retrieval to complete final egg maturation. This timing ensures eggs reach the optimal developmental stage for collection.
- Procedure: A reproductive specialist inserts an ultrasound-guided needle through the vaginal wall into each ovary to aspirate follicular fluid containing mature eggs. The needle extracts fluid from each developed follicle visible on ultrasound imaging.
- Recovery: Most patients rest 2 to 4 hours post-procedure before discharge home. Mild cramping and light spotting occur for 1 to 2 days following retrieval.
3. Sperm Collection or Retrieval
Sperm samples are obtained on egg retrieval day to maintain optimal freshness for fertilisation procedures in the laboratory. The IVF ICSI procedure demands high-quality sperm for successful embryo creation.
- Collection Method: Partners provide fresh semen samples through masturbation after 2 to 5 days of abstinence from ejaculation. Samples are collected in sterile containers within the clinic collection rooms.
- Surgical Retrieval: Testicular sperm extraction removes sperm directly from testicular tissue when ejaculation samples are unavailable due to blockages or absence. Percutaneous epididymal sperm aspiration uses fine needles to collect sperm from the epididymis.
- Quality Check: Laboratory embryologists process collected samples to isolate motile sperm with normal morphological characteristics through washing and concentration techniques. Only the healthiest sperm are selected for fertilisation attempts.
4. Fertilisation and Embryo Development
Retrieved eggs combine with prepared sperm in laboratory dishes containing culture media that replicate fallopian tube conditions. The conventional IVF procedure places approximately 50,000 to 100,000 sperm with each egg.
Intracytoplasmic sperm injection directly injects one selected sperm into each mature egg using microscopic needles under high magnification. This IVF treatment process becomes necessary when sperm counts are low or motility is poor.
- Fertilisation Check (Day 1): Embryologists examine eggs 16 to 18 hours after sperm introduction to confirm normal fertilisation, indicated by 2 pronuclei. Pronuclei contain genetic material from both egg and sperm before fusion.
- Cell Division (Day 3): Embryos contain six to eight cells after division at the cleavage stage of development. Laboratory staff grade embryos based on cell number, symmetry, and fragmentation levels to predict viability.
- Blastocyst Stage (Day 5): Embryos develop into blastocysts containing 100 to 150 cells with distinct inner cell mass formation. Blastocyst transfers achieve higher implantation rates than Day 3 embryo transfers across patient populations.
Preimplantation genetic testing screens embryos for chromosomal abnormalities or inherited genetic conditions before transfer decisions. Tested embryos undergo freezing while awaiting results.
5. Embryo Transfer Procedure
The embryo transfer procedure places 1 or 2 selected embryos into the uterine cavity using thin flexible catheters without anaesthesia requirements. This painless process takes 5 to 10 minutes to complete.
- Timing: Fresh embryo transfers occur 3 days after egg retrieval at the cleavage stage or 5 to 6 days later at the blastocyst stage. Frozen embryo transfers happen during subsequent cycles after endometrial preparation with oestrogen and progesterone supplementation.
- Procedure: Physicians insert a speculum and clean the cervix before passing soft catheters loaded with embryos through the cervical opening. Abdominal ultrasound guidance ensures embryo placement 1 to 2 centimetres from the uterine fundus.
- Aftercare: Patients rest 15 to 30 minutes after transfer before resuming normal daily activities without restrictions. Progesterone supplementation continues for 8 to 12 weeks, supporting uterine lining and early pregnancy development.
The complete IVF procedure steps from stimulation initiation to pregnancy testing span approximately four to six weeks for fresh cycles. Blood pregnancy tests measure beta-hCG levels nine to fourteen days after transfer.
IVF Procedure Success Rate and Factors That Influence It
The IVF success rate fluctuates based on patient age, embryo quality, and clinic protocols used during treatment cycles.
- Age: Female age is the strongest predictor of IVF procedure outcomes due to declining egg quality and quantity after 35 years. Women under 35 achieve 55% IVF success rates per transfer cycle, while those aged 35 to 38 see 40% success rates, and women aged 38 to 40 experience 26% success rates.
- Embryo Quality: Morphological grading evaluates cell number, symmetry, and fragmentation to predict implantation potential before transfer decisions. Blastocyst transfers show higher success rates than Day 3 embryo transfers.
At Ferticity, our team brings over 40 years of combined clinical experience to every treatment cycle. We have completed more than 17,800 IVF and ICSI procedures with success rates between 70 to 80%. Our 58,000+ patients have benefited from personalised protocols and advanced laboratory capabilities.
Conclusion
The IVF procedure represents a scientifically refined series of medical interventions designed to overcome infertility barriers through controlled fertilisation and embryo development. Since 1978, these five stages have led to millions of births worldwide, changing reproductive medicine and providing real chances for parenthood. The test tube baby process remains the most effective assisted reproductive technology for couples facing conception challenges.
Book your IVF consultation today and take the next step towards parenthood.
FAQs
- How long does the IVF process take from start to finish?
One complete IVF cycle requires 4 to 6 weeks from medication start to pregnancy test, including 8 to 14 days of ovarian stimulation, egg retrieval, 3 to 6 days of embryo development, and 9 to 14 days post-transfer before testing.
- How many eggs are usually collected during an IVF procedure?
Doctors collect 8 to 15 mature eggs on average, depending on ovarian response to stimulation medications. Approximately 70 to 80% of mature eggs fertilise normally, and 30 to 50% develop into viable blastocysts.
- Is IVF painful?
Ovarian stimulation injections cause minor discomfort at injection sites similar to routine vaccinations. Egg retrieval performed under sedation produces cramping for one to two days afterwards. The embryo transfer procedure is painless and requires no anaesthesia.
- Can an IVF procedure guarantee pregnancy?
IVF increases conception chances but cannot guarantee pregnancy due to biological factors affecting implantation and early development. Success depends on age, embryo quality, uterine receptivity, and overall reproductive health.
- How is IUI different from IVF?
The IUI procedure, step by step, places washed sperm directly into the uterus during natural ovulation, while IVF fertilises eggs outside the body in laboratory conditions. IUI represents a less invasive approach with success rates typically between 5 to 20% per cycle compared to IVF’s higher rates.