Fallopian tube sterilization, also known as tubal ligation, is a permanent method of birth control in women. However, some women who have undergone sterilization may wish to become pregnant later in life. In such cases, fallopian tube sterilization reversal may be considered. In this blog, we will discuss how fallopian tube sterilization reversal is done.
What is Fallopian Tube Sterilization Reversal?
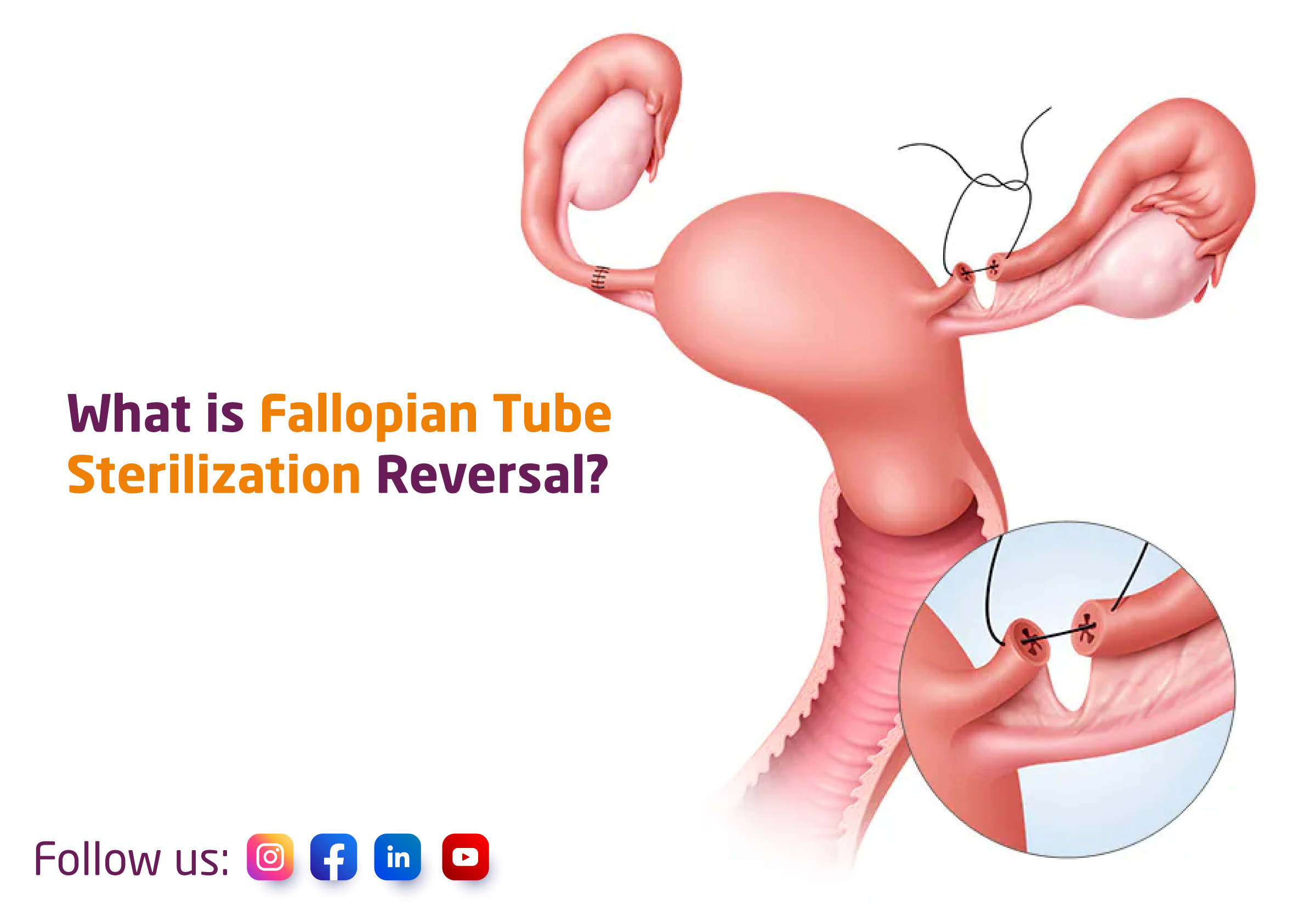
Fallopian tube sterilization reversal is a surgical procedure that aims to restore the function of the fallopian tubes after they have been blocked or cut during a previous sterilization surgery. During the procedure, the blocked or cut portions of the fallopian tubes are reconnected to allow the eggs and sperm to meet, leading to natural fertilization and pregnancy.
Who is a Candidate for Fallopian Tube Sterilization Reversal?
Women who have undergone tubal ligation and wish to become pregnant again may be candidates for fallopian tube sterilization reversal. The success of the procedure depends on various factors, such as the woman’s age, her egg reserve, the type of sterilization procedure performed, the length and quality of the remaining fallopian tube segments, and the fertility of the partner. Therefore, it is important to discuss the potential benefits and risks of the procedure with a specialist.
How is Fallopian Tube Sterilization Reversal Done?
Fallopian tube sterilization reversal is a delicate surgical procedure that requires the expertise of a skilled surgeon. This technique involves reconnecting the severed ends of the fallopian tubes. The surgery can be performed with laparoscopy, that is by making a small slit in your belly and placing the camera and other instruments through it or by open incision that is by giving a small incision on the lower abdomen and visualizing the tubes directly. The blocked portions of the tubes are then cut and removed, and the remaining healthy segments are rejoined using microsurgical techniques. Then, dye is injected to check for the patent of the tubes. This technique has a high success rate, with about 50-80% of women achieving pregnancy after the procedure.
Recovery and Follow-Up
After the surgery, the woman will need to rest for a few days and avoid heavy lifting and strenuous activity for a few weeks. Pain medication and antibiotics may be prescribed to manage pain and prevent infection. Follow-up appointments with the specialist will be necessary to monitor the healing process and assess fertility.
In conclusion, fallopian tube sterilization reversal is a viable option for women who wish to become pregnant after undergoing tubal ligation. The success of the procedure depends on various factors, and the decision to undergo surgery should be made after careful consideration and consultation with a specialist. With proper technique and follow-up, fallopian tube sterilization reversal can be a safe and effective way to achieve pregnancy.