Egg and embryo freezing, also known as oocyte cryopreservation and embryo cryopreservation, respectively, are two techniques used to preserve a woman’s fertility. These methods are particularly useful for women who want to delay pregnancy, have a medical condition that affects their fertility or want to preserve their fertility before undergoing cancer treatment. In this blog, we’ll discuss how egg and embryo freezing are done and what to expect during the process.
Egg Freezing (Oocyte Cryopreservation)
Egg freezing is a procedure that involves extracting a woman’s eggs from her ovaries and freezing them for later use. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how egg freezing is done:
- Ovarian Stimulation
The first step in egg freezing is ovarian stimulation. Women typically produce one egg per menstrual cycle. However, to increase the chances of success in egg freezing, multiple eggs need to be collected. To achieve this, the woman is given hormones to stimulate her ovaries to produce several eggs at once. Hormonal medications, such as follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), Human menopausal gonadotropin (HMG) or luteinizing hormone (LH), are typically used for this purpose.
2. Egg Retrieval
Once the woman’s ovaries have developed multiple eggs, they are ready for retrieval. This is typically done via transvaginal ultrasound-guided aspiration, a minimally invasive procedure in which a needle is inserted through the vaginal wall into the ovary to retrieve the eggs. General anaesthesia is typically used during this procedure, which takes 15-30 minutes.
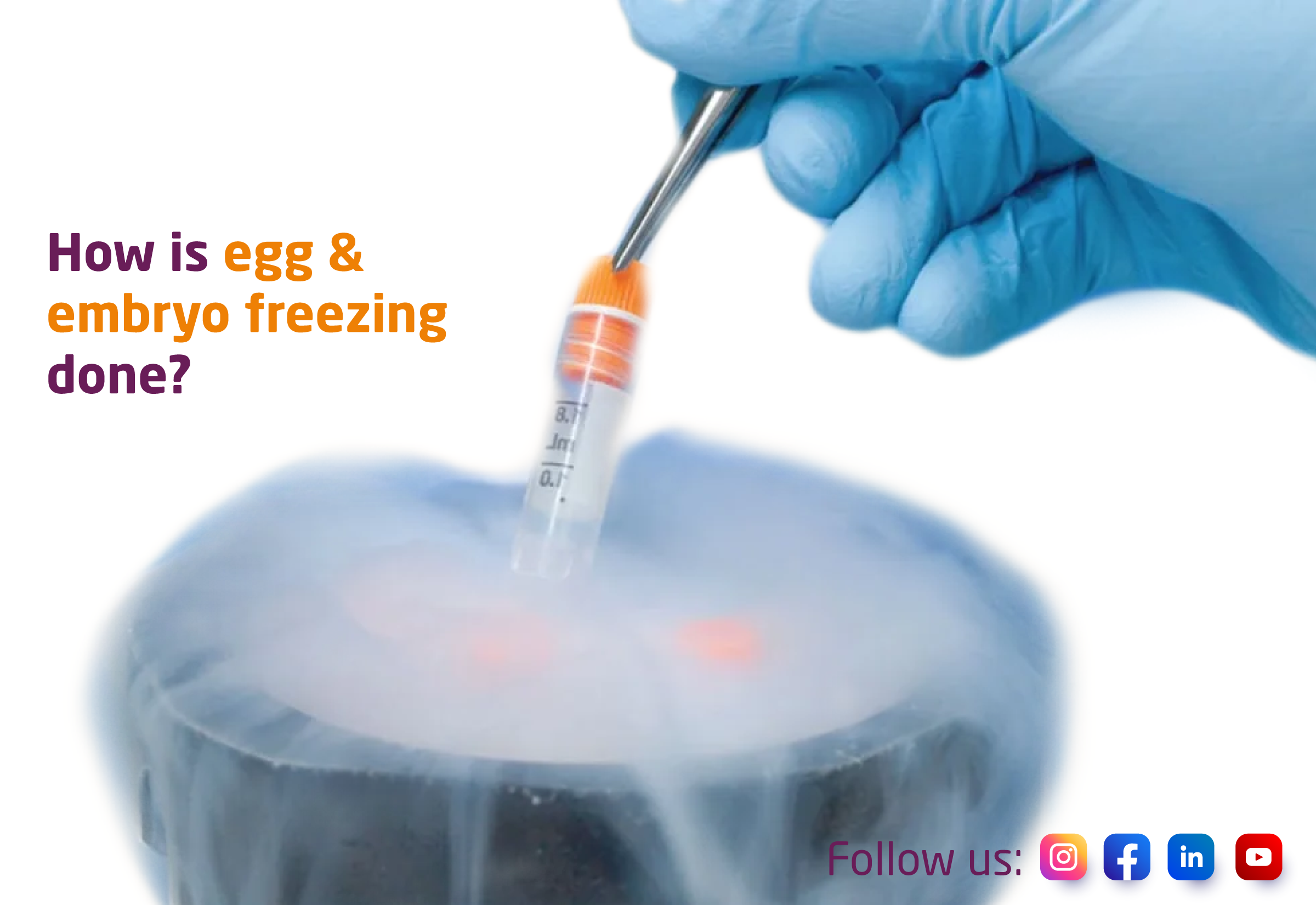
3. Egg Freezing
After the eggs are retrieved, they are immediately frozen using a technique called vitrification. Vitrification is a flash-freezing technique that involves rapidly cooling the eggs too -196°C in liquid nitrogen. This process prevents the formation of ice crystals, which can damage the eggs.
4. Egg Storage
Once the eggs are frozen, they are stored in a cryopreservation facility until they are needed. The eggs can be stored for up to 10 years. However, if required, this period can be extended further, after taking permission from an appropriate authority.
Embryo Freezing (Embryo Cryopreservation)
Embryo freezing is a procedure that involves fertilizing a woman’s eggs with sperm outside of the body and freezing the resulting embryos for later use. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how embryo freezing is done:
- Ovarian Stimulation and Egg Retrieval
Like egg freezing, the first step in embryo freezing is ovarian stimulation. Hormonal medications are used to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs, which are then retrieved via transvaginal ultrasound-guided aspiration.
2. Fertilization
After the eggs are retrieved, they are fertilized with sperm in a laboratory dish. This can be done using two methods: conventional IVF (in vitro fertilization) or ICSI (intracytoplasmic sperm injection). In conventional IVF, the eggs and sperm are mixed together in a dish and left to fertilize naturally. In ICSI, a single sperm is injected directly into each egg.
3. Embryo Culture
After fertilization, the resulting embryos are cultured in the laboratory for several days. During this time, the embryos are monitored to ensure that they are developing normally.
4. Embryo Freezing
Once the embryos have reached a certain stage of development, they are frozen using vitrification. Like with egg freezing, the embryos are rapidly cooled to -196°C in liquid nitrogen to prevent ice crystal formation.
5. Embryo Storage
The frozen embryos are then stored in a cryopreservation facility until they are needed. Like eggs, embryos can also be kept frozen for up to 10 years and if required the duration can be extended after taking permission from an appropriate authority.
What are the uses of egg and embryo freezing?
Egg and embryo freezing, also known as oocyte and embryo cryopreservation, are methods of preserving reproductive cells/embryos for future use. Here are some of the uses of egg and embryo freezing:
- Fertility preservation: Egg and embryo freezing allow individuals to preserve their fertility for later use, especially in cases where medical treatments such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy may damage their reproductive cells.
- Delayed childbearing: Egg freezing can be used by women who want to delay childbearing for personal or professional reasons. By freezing their eggs at a younger age, they can increase their chances of having a healthy pregnancy in the future.
- Genetic testing: Embryos can be frozen to allow time for genetic testing to be conducted, which can help identify any potential genetic abnormalities or inherited diseases.
Overall, egg and embryo freezing can provide individuals with more options for family planning and fertility treatment.
Are there any side effects of egg and embryo freezing?
Egg and embryo freezing are generally safe and do not have significant side effects. However, as with any medical procedure, there may be some risks and potential side effects. Here are some possible side effects during the procedure of egg and embryo freezing:
- Discomfort or pain: Some women may experience discomfort or pain during the egg retrieval process, which involves using a needle to extract the eggs from the ovaries.
- Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS): In rare cases, the medications used to stimulate the ovaries to produce more eggs can lead to OHSS, which is characterized by abdominal pain, bloating, and nausea.
- Emotional stress: The process of undergoing egg or embryo freezing can be emotionally stressful, as it involves decisions about family planning and fertility treatment.
- Failed cycles: There is a possibility that some eggs or embryos will not survive the freezing and thawing process.
- It is important to discuss the potential risks and benefits of egg and embryo freezing with a doctor to make an informed decision about whether it is the right option for you.
Conclusion
Egg and embryo freezing are two techniques that allow women to preserve their fertility for later use. Egg freezing involves extracting a woman’s eggs, freezing them using vitrification, and storing them until needed.
Embryo freezing involves fertilizing a woman’s eggs with sperm outside the body, freezing the resulting embryos using vitrification, and storing them until needed. Both techniques can be done for a variety of reasons and have varying success rates depending on various factors.
Overall, egg and embryo freezing offers women the option to delay pregnancy or preserve their fertility in the face of medical or personal circumstances.